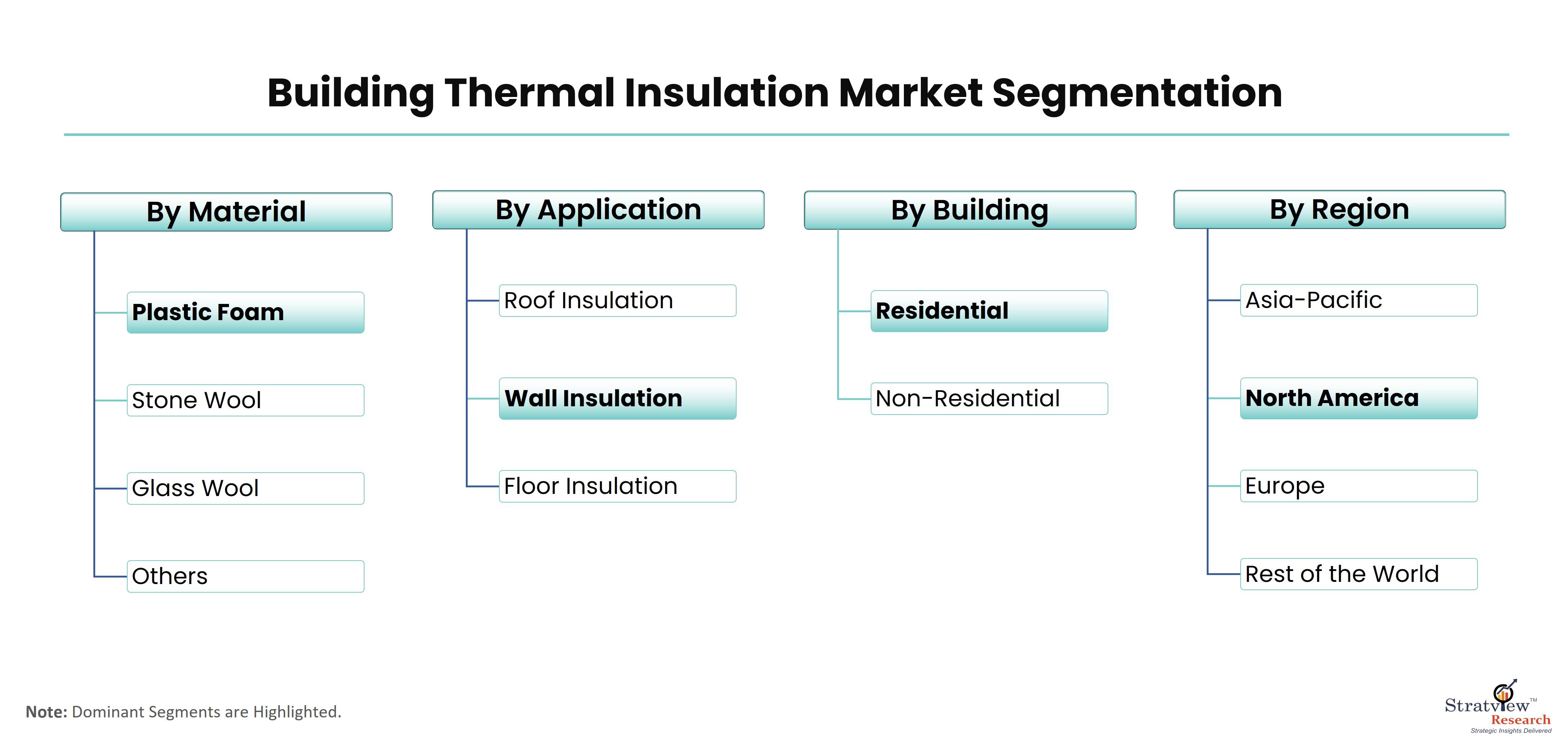
According to Stratview Research, the building thermal insulation market was estimated at USD 28.06 billion in 2022 and is likely to grow at a CAGR of 4.66% during 2023-2028 to reach USD 37.01 billion in 2028.
In the realm of modern architecture and construction, the concept of comfort extends far beyond mere aesthetics. It encompasses a harmonious balance between temperature, humidity, and air quality within indoor spaces. At the heart of this equilibrium lies building thermal insulation, a fundamental component that has undergone a remarkable evolution over the years. In this article, we delve into the dynamic landscape of building thermal insulation, tracing its evolution, exploring innovative trends, and highlighting its pivotal role in redefining comfort in contemporary buildings.
The Evolution of Thermal Insulation:
The history of thermal insulation can be traced back centuries, with ancient civilizations employing natural materials such as straw, mud, and animal hides to regulate indoor temperatures. However, it wasn't until the Industrial Revolution that significant advancements were made in insulation materials and techniques. The widespread adoption of mass-produced building materials like bricks, glass, and metals necessitated the development of new insulation solutions to improve thermal comfort and energy efficiency.
The early 20th century saw the emergence of materials like mineral wool, fiberglass, and cellulose insulation, which offered improved thermal performance and durability compared to traditional alternatives. These materials became synonymous with modern construction practices and laid the foundation for the evolution of thermal insulation in the decades to come.
Innovative Materials and Technologies:
In recent years, rapid advancements in material science and engineering have fueled a wave of innovation in the field of thermal insulation. New materials such as spray foam insulation, aerogels, and vacuum insulated panels (VIPs) have revolutionized the way buildings are insulated, offering higher levels of thermal resistance in thinner profiles.
Spray foam insulation, for instance, is renowned for its ability to seal gaps and cracks effectively, providing superior air sealing and thermal performance compared to traditional insulation materials. Aerogels, on the other hand, boast remarkable thermal properties, with ultra-low thermal conductivity and lightweight composition, making them ideal for space-constrained applications.
Moreover, advancements in manufacturing processes have enabled the production of insulation materials with enhanced sustainability credentials. Recycled and bio-based insulation materials are gaining popularity for their reduced environmental impact and compatibility with green building standards.
Enhancing Comfort and Energy Efficiency:
Beyond its primary function of regulating indoor temperatures, thermal insulation plays a crucial role in enhancing overall comfort and energy efficiency in buildings. Properly insulated structures offer consistent indoor temperatures, reduce drafts and cold spots, and mitigate heat loss or gain through walls, roofs, and windows.
Furthermore, energy-efficient buildings with well-insulated envelopes require less heating and cooling energy, resulting in lower utility bills and reduced carbon emissions. This not only benefits building occupants in terms of comfort and affordability but also contributes to global efforts to combat climate change and promote sustainability.
Looking Ahead:
As we look to the future, the evolution of building thermal insulation shows no signs of slowing down. Continued research and innovation will drive the development of new materials, technologies, and construction techniques aimed at further improving thermal performance, durability, and sustainability.
Additionally, as climate change continues to exert pressure on the built environment, the importance of resilient and energy-efficient buildings will become increasingly apparent. Building codes, standards, and policies will likely evolve to incentivize or mandate the use of high-performance insulation solutions, further driving market demand and adoption.
In conclusion, the evolution of building thermal insulation represents a paradigm shift in the way we conceptualize and achieve comfort in the built environment. From ancient construction techniques to cutting-edge insulation materials, the journey of thermal insulation is a testament to human ingenuity and our relentless pursuit of innovation. As we continue to redefine comfort and sustainability in buildings, thermal insulation will remain a cornerstone of modern construction practices, shaping the way we inhabit and interact with our built environment for generations to come.