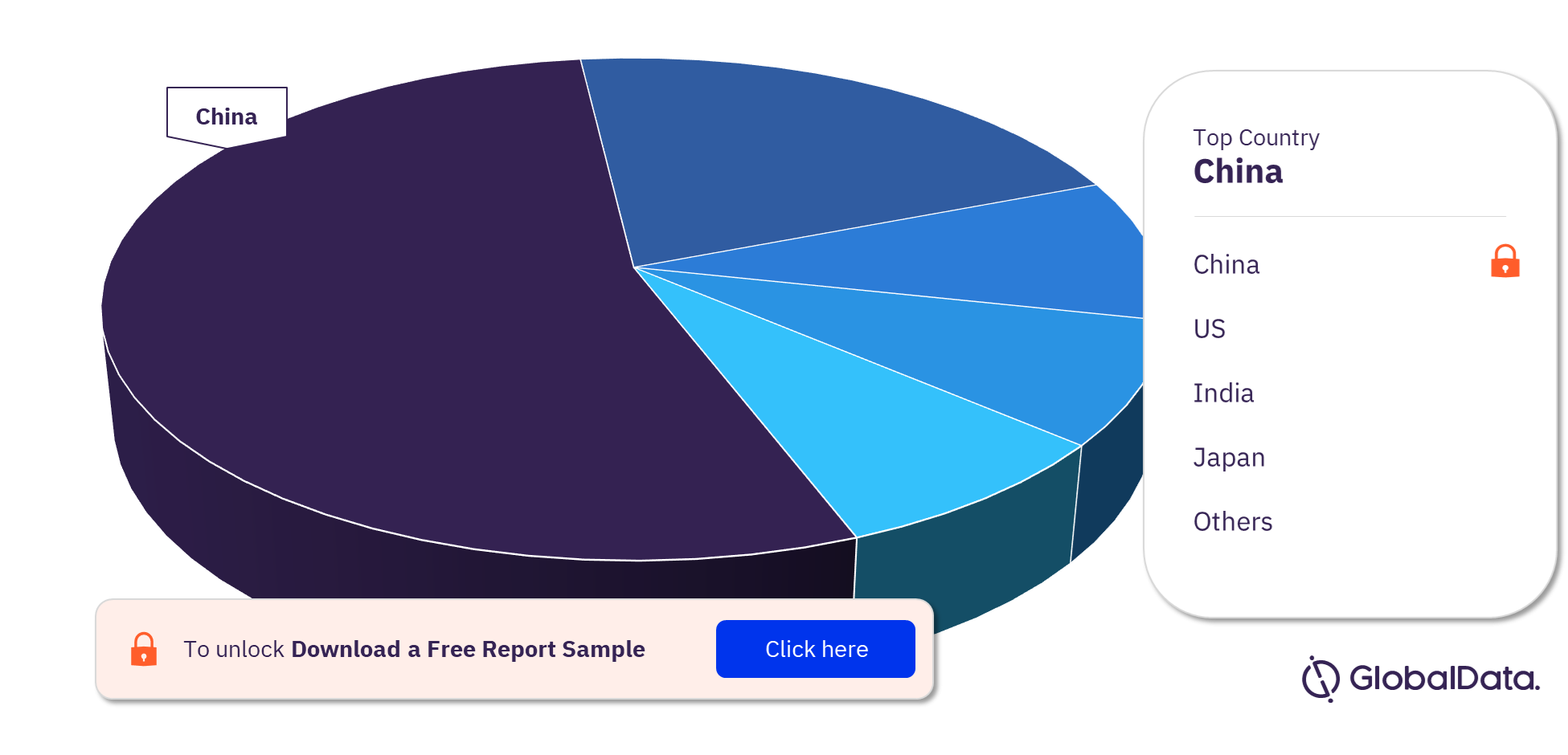
Policy and regulation play a pivotal role in shaping the growth and dynamics of the global and local solar photovoltaic (PV) markets.
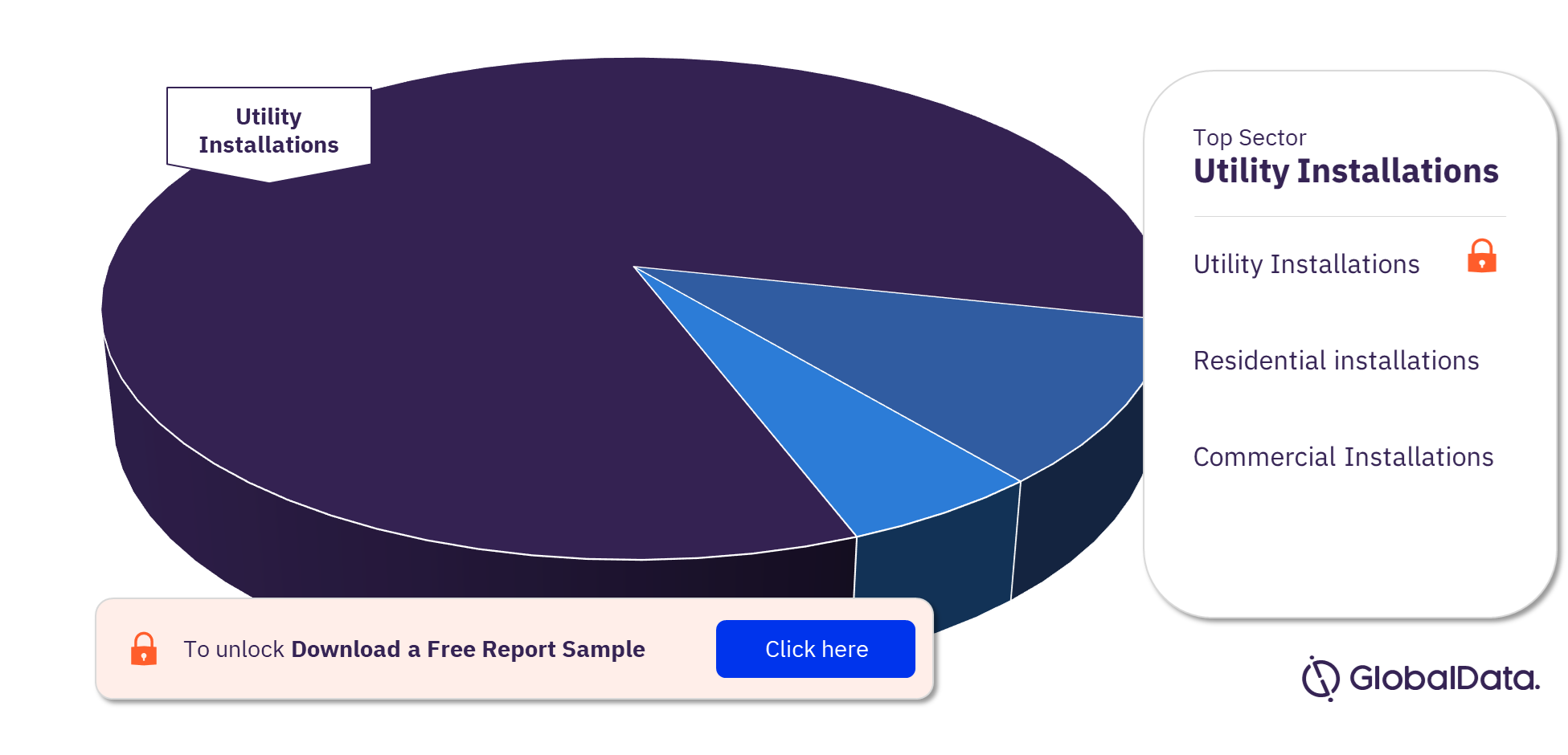
For more sector insights into the Solar PV market, download a free sample report
Here's an overview of how policies and regulations impact the solar PV market:
Global Impact:
**1. International Agreements:
- Paris Agreement: The global commitment to the Paris Agreement has spurred increased focus on renewable energy, including solar PV. Nations aim to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and supportive policies contribute to the growth of solar installations worldwide.
**2. Trade Policies:
- Tariffs and Trade Disputes: Trade policies, including tariffs on solar components, can impact the cost competitiveness of solar PV. Trade disputes, especially among major solar-producing countries, influence market dynamics and prices.
**3. Financial Mechanisms:
- Global Funding Initiatives: International funding and financial mechanisms, such as the Green Climate Fund, support solar projects in developing countries. These initiatives aim to accelerate the adoption of renewable energy and address climate change.
**4. Technology Transfer and Collaboration:
- Collaborative Research: Policies promoting technology transfer and collaborative research enhance global cooperation in advancing solar PV technologies. This fosters innovation and accelerates the development of more efficient and cost-effective solar solutions.
**5. Sustainability Goals:
- Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs): Solar PV aligns with several SDGs, including affordable and clean energy, climate action, and sustainable cities. Global initiatives and policies reflect a commitment to achieving these goals through increased solar adoption.
Local Impact:
**1. Feed-in Tariffs (FiTs) and Incentives:
- Encouraging Investments: Local policies, such as feed-in tariffs and financial incentives, encourage investments in solar PV projects. These mechanisms provide guaranteed payments for solar energy production, making projects financially attractive.
**2. Net Metering and Grid Connection Policies:
- Grid Integration: Policies supporting net metering and easy grid connection enable solar PV system owners to feed excess energy back into the grid. This promotes grid integration and makes solar energy a viable option for consumers.
**3. Renewable Portfolio Standards (RPS):
- Mandated Renewable Energy: Many regions implement RPS, requiring a certain percentage of energy to come from renewable sources, including solar. Compliance with RPS stimulates the growth of the solar PV market.
**4. Building Codes and Permitting:
- Streamlining Processes: Local building codes and permitting procedures influence the ease of installing solar PV systems. Streamlining these processes and providing clear guidelines encourage residential and commercial adoption.
**5. Community Solar Programs:
- Inclusive Energy Access: Policies supporting community solar programs make solar energy accessible to a broader population. These initiatives enable individuals without rooftop space to benefit from shared solar installations.
**6. Tax Credits and Rebates:
- Financial Incentives: Tax credits, rebates, and other financial incentives offered by local governments encourage individuals and businesses to invest in solar PV. These mechanisms reduce the upfront costs and accelerate the payback period.
**7. Energy Storage Policies:
- Integration with Storage: Policies addressing energy storage integration with solar systems contribute to grid stability and reliability. Supportive regulations can incentivize the adoption of solar-plus-storage solutions.
**8. Environmental Regulations:
- Emission Reduction Targets: Policies aimed at reducing carbon emissions and achieving environmental targets drive the adoption of clean energy sources, including solar PV. These regulations contribute to the transition to a low-carbon economy.
Challenges and Opportunities:
**1. Policy Stability:
- Challenges: Policy instability or sudden changes can create uncertainties for investors and impact project viability.
- Opportunities: Clear and stable policies provide a conducive environment for long-term investments and project planning.
**2. Grid Interconnection Challenges:
- Challenges: Grid connection policies may face challenges in accommodating the increasing number of solar installations.
- Opportunities: Updating and enhancing grid infrastructure can address interconnection challenges, ensuring efficient integration of solar PV into the grid.
**3. Inclusive Policies:
- Challenges: Ensuring inclusivity and access to solar benefits for all communities may be a challenge.
- Opportunities: Implementing policies that prioritize inclusivity and address energy poverty can open up new markets and enhance social and economic benefits.
**4. Technology-Neutral Policies:
- Challenges: Policies favoring specific technologies may hinder overall technological progress.
- Opportunities: Implementing technology-neutral policies encourages competition and innovation across various renewable energy technologies.
In conclusion, the impact of policies and regulations on the solar PV market is multifaceted. Supportive, stable, and well-designed policies can drive the growth of the solar industry, enhance energy security, and contribute to achieving global sustainability goals. On the other hand, challenges such as policy instability and grid integration issues need to be addressed to unlock the full potential of solar PV.